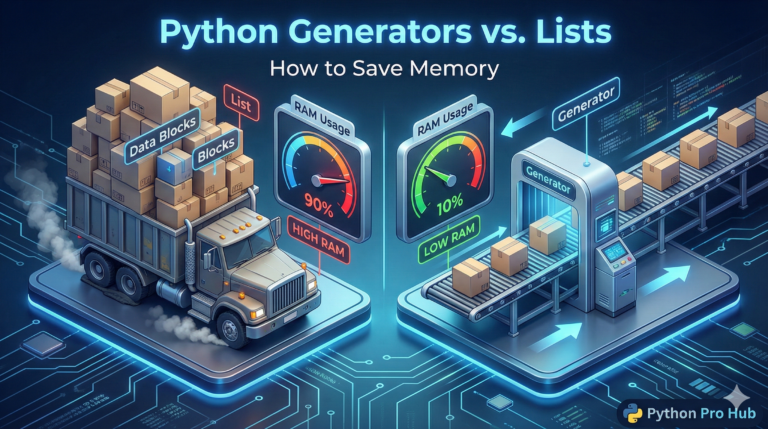
Sometimes you need a tiny function for just one quick task. Python Lambda Functions are perfect for these occasions. Writing a full def my_function(): block feels like overkill.
Enter the Lambda Function. It’s a way to write a function in a single line.
The Syntax
A lambda function can take any number of arguments, but can only have one expression. lambda arguments : expression
Normal Function vs. Lambda
# Normal way
def add_five(x):
return x + 5
print(add_five(10)) # Output: 15
# Lambda way
add_five_lambda = lambda x : x + 5
print(add_five_lambda(10)) # Output: 15When to Use Them
Lambdas are most powerful when used inside other functions that expect a function as an input, like map(), filter(), or sorting.
Example: Sorting by a specific key
Imagine you have a list of tuples, and you want to sort by the second item (the age).
students = [("Alice", 25), ("Bob", 20), ("Charlie", 30)]
# Sort by age (index 1)
# The lambda function takes a student 's' and returns 's[1]' (their age)
students.sort(key=lambda s: s[1])
print(students)
# Output: [('Bob', 20), ('Alice', 25), ('Charlie', 30)]Without lambda, you’d have to write a separate function just to tell .sort() how to look at the age.